A urinary tract infection, also known as urine infection or UTI, is an infection in any part of the urinary system that includes kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
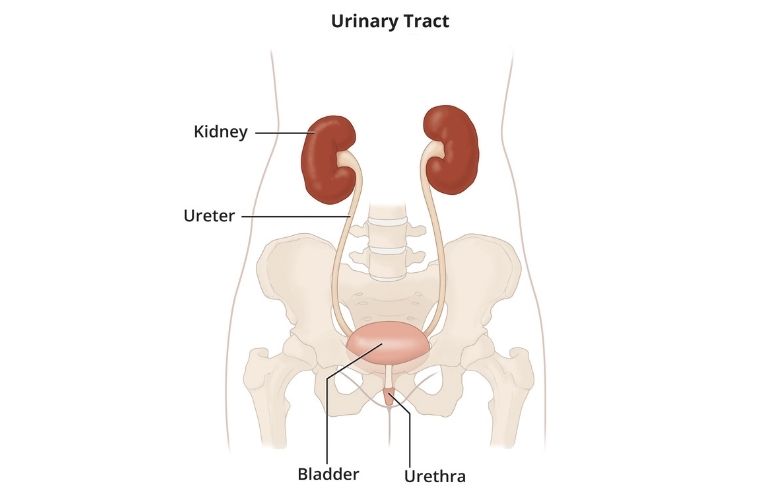
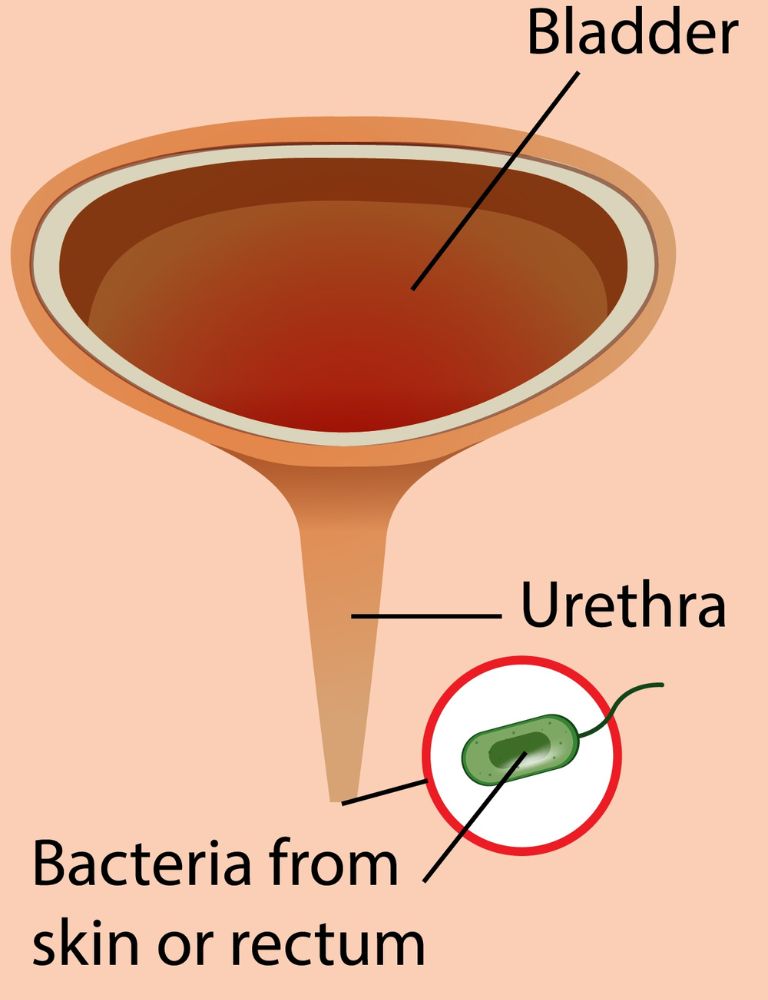
Urine infection or urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common infection found in women. The urinary tract is made up of your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and start to develop into the bladder. It can happen anywhere in your urinary tract. Urine infection is an infection from microbes, a type of organism that is too small and cannot be seen without microscopes. Along with bacteria, in some cases, viruses or fungi can also cause urinary tract infections.
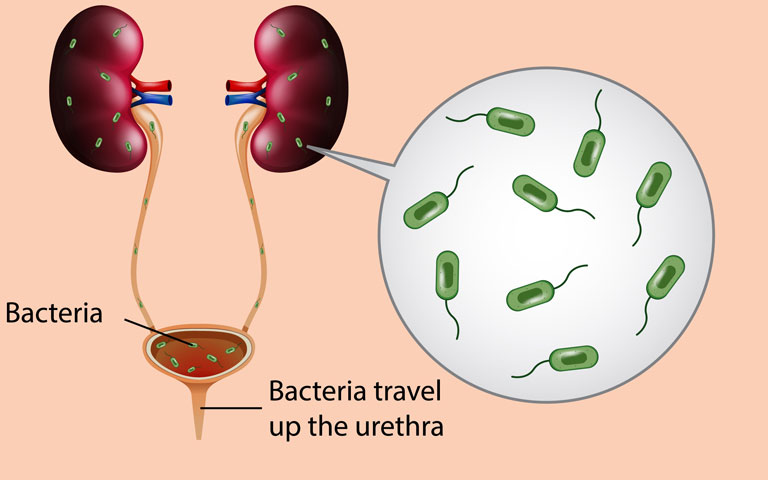
Urine infection is common in women and the following are the factors that increase the risk of getting urinary tract infection or UTI for women -
Factors like having a short urethra also play a major role in getting a UTI as it is easier for bacteria to reach the bladder due to the short distance. Also, after menopause women are more vulnerable to urine infection as they lose estrogen protection and have a change in the lining of the vagina.
Women who use certain types of birth control like diaphragms tend to have UTI. Also, using condoms with spermicidal foam or using spermicidal agents is known to be linked to a greater risk of getting UTIs in women.
If there is a natural abnormality in the urinary tract like structural abnormalities where urine cannot leave the body normally or comes back up in the urethra then chances of getting a UTI increases. Also, people using devices like catheters or tubes have an increased risk of UTIs. In addition, if one is experiencing any type of blockages like kidney stones, spinal cord injury then that also may lead to urinary tract infection.
The types of UTIs depend on which part of your urinary tract is infected. The following are the types of UTIs and their symptoms -
It is an infection in the kidneys.
This is an infection of the bladder.
This is an infection of the urethra.
Tests and procedures used to diagnose urinary tract infections include:
In cases of frequent and serious urine infections and if any serious problem is suspected with the urinary tract, an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan will be suggested to have a closer look. Along with these, a contrast dye may also be used to highlight structures in your urinary tract.
It is a long, flexible tube that is used to look inside your urethra and bladder. The doctor will suggest this in cases of recurrent UTIs.
When it comes to the treatment, urinary tract infections are usually divided into two types - simple UTIs and complicated UTIs.
These infections are simple, irregular infections that happen in healthy people with normal urinary tracts. For simple UTIs, urine infections, antibiotics are the primary course of treatment. The types of medicines and the duration of the course or treatment vary from person to person and depend upon the individual's case, requirements, and type of bacteria found in the urine sample. In cases with postmenopausal women with UTIs, topical (vaginal) hormone replacement with estrogen may also be suggested.
These infections are recurring, frequent, and problematic as they happen in abnormal urinary tracts. These infections are called complicated also because the bacteria causing such infections cannot be treated by many antibiotics. For complicated urinary tract infections, treatments like a longer course of antibiotics may be suggested where the antibiotic therapy may be started intravenously (IV) in the hospital and then after some time is continued by mouth. For postmenopausal women with severe infection, vaginal estrogen therapy is generally suggested.


Dr. Ashit Shah is a senior consultant Urologist heading Aashray Urology Institute. After completing his M.B.B.S. and M.S. in General Surgery, he was awarded Diplomate of National Board (D.N.B.) in Genito-Urinary Surgery by the National Board of Examinations, New Delhi. He earned his Diplomate in Laparoscopic Urology from Louis Pasteur University, Strasbourg, France in the year 2006. Dr. Shah has a special interest in Endo-Urology, especially Urolithiasis i.e. Urinary Stone Disease. Having spent more than 27 years in the profession of Urology, he has experience of over 75,000 urological consultations and more than 15,000 surgeries. Being counted amongst the torch bearers of ethical and transparent medical practice in the city of Vadodara, he was conferred ‘Inspiring Urologist Award’ for the year 2019 by The Economic Times.