Urinary Incontinence or UI is basically a loss of bladder control. It is a common problem found in women wherein unintentional loss of urine can be occasional or serious, caused by various factors. UI can be treated with a number of treatments depending upon its causes and severity.
Urinary Incontinence (UI) is the involuntary or unintentional leakage of urine. It is a common and treatable problem. The factors like age, pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, weakened control over the urinary sphincter contribute majorly to involuntary loss of urine. The severity of UI differs from person to person and can vary in the range from occasionally leaking the urine when one coughs or sneezes to regularly having a sudden and uncontrollable urge to urinate.
The following are the factors that increase the risk of developing urinary incontinence -
If UI runs in the family or a close relative has urinary incontinence, the chances or risk of developing UI increases.
Inability to control the bladder and involuntary leakage of urine can happen as the muscles in the bladder and urethra start losing their strength and weaken with age. Hence, old age is considered a common risk factor for UI. Along with these common problems, some diseases and conditions like diabetes, kidney disease, spinal cord injury, and neurologic diseases can also increase the risk of UI.
Urinary incontinence can be found in both men and women; however, it is most commonly found in women as factors like normal female anatomy, pregnancy, childbirth, menopause increase the risk of UI.
Obesity or extra weight adds pressure on the bladder and its surrounding muscles, weakening them. This increases the risk of involuntary leakage of urine when one coughs or sneezes.
The continuous usage of tobacco as well as a chronic cough, a side-effect of smoking, may result in episodes of incontinence and increase the risk of urinary incontinence.
In this type of incontinence, urine leaks when the pressure is added or increased on the bladder by sudden movements or physical activities. The term “stress” here refers to added physical pressure on the bladder and muscles involved in urinary control. Loss of urine happens in such cases because the actions or movements make weak pelvic floor muscles add pressure on the bladder & urethra and work them harder.
The following physical movements or sudden actions are symptoms/ triggers for stress incontinence -

In this common type of incontinence, unintentional leakage of urine happens during or after a strong, sudden, and uncontrollable urge to urinate. During such intense urges, one may not always necessarily reach the bathroom in time, and in most cases, if she does, she is not able to urinate much. In urge incontinence, one may feel the need to urinate frequently like 8 or more times a day or throughout the night when it is least expected. It is also called an “overactive bladder.”
The following are the triggers for urge incontinence -

In this type of incontinence, constant leakage or loss of urine in small amounts is experienced. This constant dribbling happens due to the inability to empty the bladder completely or obstruction/ blockage to the bladder.
In this type of incontinence, loss of urine happens due to a lack of control over the bladder. In total incontinence, the bladder is unable to store urine, resulting in episodes of unintentional leakage of urine wherein the one person leaks urine continuously or has periodic uncontrollable leaking of large amounts of urine.
The following are the triggers for total incontinence -
In this type of incontinence, urine leakage happens as a result of the inability to reach the bathroom in time and other such issues due to mental or physical impairment.
Many women experience this type of incontinence. As the name suggests, it is a combination of different types of incontinence. Most commonly, mixed incontinence refers to a combination of stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
The symptoms and causes for this type of incontinence are those of stress as well as urge incontinence.
It is important to understand the cause/s and type of incontinence to determine the right and most suitable treatment option. During a health checkup, the doctor will discuss your symptoms, pattern, and medical history to understand and determine the type of incontinence and treatment. You may also have to go through a physical examination wherein you will be asked to do certain movements or activities like coughing to determine the type, symptoms, and type of incontinence and demonstrate the same.
If the type and treatment is not defined and decided upon in the initial health checkup, you may be asked to go through the following tests -
You will be asked to record your fluid intake, how much and how many times you urinate, patterns, urges, and other such factors.
The sample of your urine will be taken to check the signs of infection and other such causes of incontinence.
Images of kidneys, bladder etc. will be taken with the help of an ultrasound wand to detect unusual symptoms or activities that may be causing urinary incontinence.
During this test, you will be asked to try different positions and movements like coughing as the doctor checks for urine loss.
In this test, a thin tube with a tiny camera will be inserted into the urethra and bladder to look for unusual symptoms, damage etc. Depending upon the type of test, local or general anesthesia will be given.
During this test, pressure in the bladder and the flow of urine will be checked with the help of various techniques.
You will work with your doctor to come up with the most suitable treatment plan for you. Depending upon the underlying cause, symptoms, and severity of incontinence, these treatments may vary or a combination of treatments may be suggested. The treatment generally will start with non-invasive options and move on to the other options if those fail to treat your incontinence.
In this training, you will be expected to learn to control the number of times you go to the bathroom and urge to urinate. You may also be asked to keep a diary to keep a record, write down details, and understand how you can change your habits. Bladder training helps the bladder to stretch itself and hold more urine in it.
Double voiding basically means emptying the bladder twice. In this training, you will try to empty your bladder completely by urinating once and then urinating again after a few minutes.
In this training, you will keep a schedule as to when and how often you can go to the bathroom. Also, you will be asked to make delays, lengthen the time between bathroom breaks etc. You will train you and your bladder to control the urge and keep the urine in by doing this.
You will be given instructions like cutting down alcohol, caffeine, acidic food, stop smoking, limit liquid consumption, and specific instructions as per your needs and requirements. You will also be asked to increase physical activity and lose weight as it plays a major role in managing incontinence.
You may also be suggested pelvic floor exercises or kegel exercises. These exercises strengthen the muscles that help control urination which over time with aging or after childbirth become weak.
Medications like Anticholinergics, Mirabegron help to control the overactive bladder, increase its capacity to hold the amount of urine, and empty it completely. Topical estrogen is also used in the form of vaginal cream or patches to tone up the muscles, tissues in the vaginal area, urethra, and help in better management of urinary incontinence. In addition to these options, sometimes botox is also used to treat urinary incontinence as it helps to relax the overactive bladder.
There are certain medical devices that are inserted into the urethra in order to help women with incontinence. These devices include:
It is a small, tampon-like disposable device. It can be inserted into the urethra before a specific activity that may trigger incontinence; so, it can act as a barrier to prevent leakage and be removed conveniently.
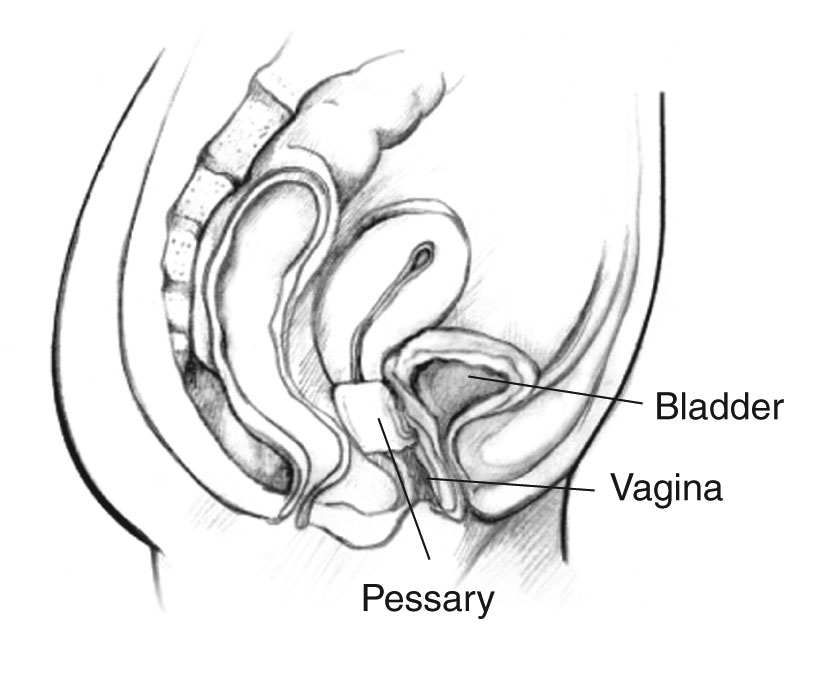
This flexible, silicone ring-like device is used as a support in case the bladder has prolapsed (dropped) or vaginal prolapse. It supports the urethra and prevents the loss of urine.
Electrical pulses or gentle electric stimulation can be helpful to stimulate, change the bladder’s reaction, strengthen pelvic floor muscles, and control incontinence. This treatment is not applicable for stress incontinence. There two types in this type of treatment -
In this procedure, a stimulator is implanted in the lower back where the sacral nerve is located. From there, the stimulator sends gentle electric pulses from the bladder to the brain indicating when the time to urinate comes. These pulses also release pain-blocking agents and help to strengthen your pelvic muscles and increase blood flow to your bladder.
In this procedure, a stimulator is implanted in the ankle where the tibial nerve is located. From there, the stimulator sends electrical stimulation to the spine, where it affects the nerves that control your bladder.
This treatment is only applicable for stress incontinence. In this treatment, bulking agents like fillers, botox, collagen, carbon beads are injected into the tissue surrounding the urethra. This helps to keep the urethra closed and prevent leakage of urine as these agents plump up the tissues where urine is released from your bladder, and help hold it in.
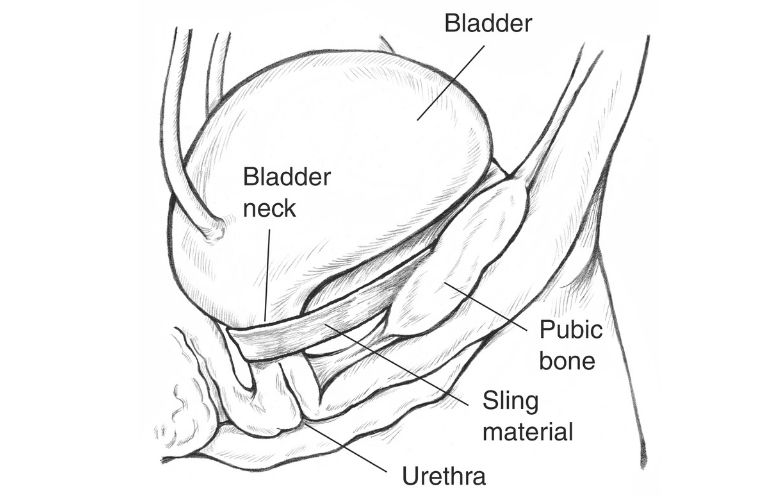
This is the most common procedure performed for urinary incontinence. Local anesthesia is used in this surgery. In this procedure, mesh (synthetic material) or strips of the body’s tissues are used to create a sling or a hammock which will create a support for the urethra and keep it closed. This prevents leakage in cases of sudden actions or changes in the position.
For this surgery, general or spinal anesthesia is used. In this procedure, support is provided through an abdominal incision to the urethra and bladder neck to control the overactive bladder.
This surgery is performed in combination with some other treatment to fix a prolapsed bladder or dropped bladder. In this surgery, stitches or sutures are used to lift up and support the tissues at the entrance of the dropped bladder.
It is a small fluid-filled ring that is implanted around the bladder neck to keep the urinary sphincter shut until there's a need to urinate.
If medical treatments do not work or as a preventive measure alongside any treatment you can use pads or catheters as extra measures.
Pads, protective garments, or absorbent panties are thin, comfortable, and convenient for everyday use. They are easily available, discreet, and can be used anytime.
If the problem is not constant or accidental leakage but the bladder’s inability to empty itself completely, then you may be suggested a catheter. It is a thin, soft tube that is to be inserted into the urethra as many times as required. This catheter helps to drain the bladder completely. These are convenient and safe to use as they are easy to insert, clean, and are reusable,


Dr. Ashit Shah is a senior consultant Urologist heading Aashray Urology Institute. After completing his M.B.B.S. and M.S. in General Surgery, he was awarded Diplomate of National Board (D.N.B.) in Genito-Urinary Surgery by the National Board of Examinations, New Delhi. He earned his Diplomate in Laparoscopic Urology from Louis Pasteur University, Strasbourg, France in the year 2006. Dr. Shah has a special interest in Endo-Urology, especially Urolithiasis i.e. Urinary Stone Disease. Having spent more than 27 years in the profession of Urology, he has experience of over 75,000 urological consultations and more than 15,000 surgeries. Being counted amongst the torch bearers of ethical and transparent medical practice in the city of Vadodara, he was conferred ‘Inspiring Urologist Award’ for the year 2019 by The Economic Times.